Introduction
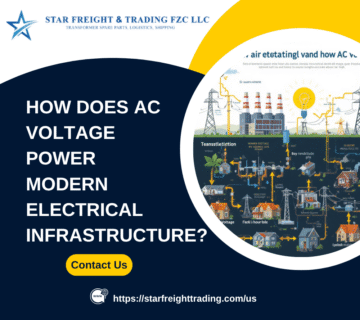
The United States’ power infrastructure relies on both alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) voltage systems to support its vast energy and industrial sectors. AC voltage is the standard for power distribution nationwide, while DC voltage is critical for applications such as renewable energy storage, telecommunications, and electric vehicles. Understanding the differences between these two power types is essential for optimizing energy efficiency, reliability, and performance in industrial and commercial settings.
Both AC and DC voltage serve distinct roles in power transmission, industrial applications, and consumer electronics. Their management requires advanced transformer technology, efficient power systems, and strategic planning to meet the growing energy demands across the U.S.
Key Differences Between AC Voltage and DC Voltage
1. Nature of Electrical Flow
AC Voltage: Alternating current periodically reverses direction, allowing it to travel long distances with minimal energy loss. It is the standard for electricity distribution across the United States.
DC Voltage: Direct current flows in one direction, making it suitable for applications requiring stable voltage, such as battery storage and electronic devices.
2. Transmission Efficiency
AC Voltage: More efficient for long-distance transmission due to lower resistive losses. The national grid in the U.S. primarily operates on AC voltage for effective power distribution.
DC Voltage: Requires specialized infrastructure for long-distance transmission. However, HVDC (high-voltage direct current) systems are increasingly used to improve efficiency in connecting remote renewable energy sources.
3. Transformer Compatibility
AC Voltage: Easily transformed to different voltage levels using transformers, which is critical for power distribution networks.
DC Voltage: Cannot be directly transformed using conventional transformers, requiring additional conversion equipment like inverters and rectifiers.
4. Applications in the U.S. Power Systems
AC Voltage Applications:
- Power transmission and distribution across cities and states
- Industrial facilities and manufacturing plants
- Household and commercial electrical systems
DC Voltage Applications:
- Renewable energy storage (solar panels, wind farms)
- Electric vehicle charging stations
- Telecommunications and data centers
Role of Transformers in Managing AC and DC Voltage in the U.S.
Transformers regulate voltage levels, ensuring efficiency and stability within the U.S. power grid. Various transformer technologies support both AC and DC voltage applications:
AC Transformers
- Step-Up Transformers: Increase voltage for efficient transmission over long distances
- Step-Down Transformers: Reduce voltage to safer levels for industrial and residential use
- Distribution Transformers: Ensure stable voltage supply to commercial and industrial sectors
DC Power Conversion Systems
- Rectifiers: Convert AC to DC for battery storage and electronic applications
- Inverters: Convert DC to AC for integration with the national power grid
- HVDC Converters: Enable efficient long-distance DC transmission, especially for renewable energy projects
Impact on the U.S. Industrial and Energy Sectors
The United States benefits from a combination of AC and DC power systems. The transition toward renewable energy and electric mobility has increased the demand for efficient DC power management while maintaining the reliability of AC voltage systems.
Integration of Renewable Energy
The U.S. is investing heavily in solar and wind energy, requiring efficient DC voltage management. Solar power plants generate DC electricity, which is converted to AC for grid distribution using advanced transformer and inverter technologies.
Industrial and Commercial Applications
Manufacturing plants, construction sites, and commercial facilities primarily rely on AC voltage for daily operations. However, DC power solutions are gaining traction for backup power, automation systems, and smart grid technologies.
Future Trends in AC and DC Power Systems in the U.S.
Advancements in HVDC Technology
The U.S. is expanding HVDC transmission lines to improve energy efficiency, particularly for interstate power distribution and integrating offshore renewable energy projects.
Smart Grid Innovations
Digital monitoring, AI-powered energy management, and real-time voltage regulation are transforming the future of power distribution in America.
Growth of Electric Vehicles (EVs)
The rise of EV adoption in the U.S. is driving demand for DC charging infrastructure, supported by advanced transformers and power converters.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between AC and DC voltage is crucial for optimizing the U.S. power systems. While AC remains the dominant form of electricity distribution, DC voltage is gaining significance in renewable energy, electric vehicles, and advanced industrial applications. By investing in cutting-edge transformer technology and smart grid solutions, the United States ensures a sustainable and resilient energy future.




No comment