Introduction
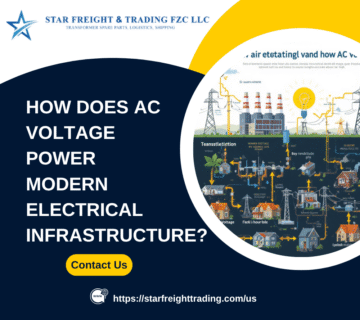
The industrial and energy sectors in the United States depend on both alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) voltage to power infrastructure, manufacturing facilities, and commercial operations. AC voltage remains the backbone of the national power grid, ensuring efficient electricity transmission across states. Meanwhile, DC voltage plays a crucial role in renewable energy systems, telecommunications, and the growing electric vehicle (EV) market.
Understanding the role of AC and DC voltage in the U.S. energy landscape is essential for optimizing power efficiency, sustainability, and technological advancements. As industries and utilities continue integrating advanced energy solutions, balancing both voltage types effectively is a priority for economic and environmental progress.
Key Differences Between AC and DC Voltage
- Nature of Electrical Flow
- AC Voltage: Alternates direction periodically, making it ideal for long-distance transmission with reduced energy loss. This is the standard electricity form used in the U.S. national grid.
- DC Voltage: Flows in a single direction, providing a stable power source for applications like solar energy storage, electronic devices, and EV charging stations.
- Transmission and Distribution Efficiency
- AC Voltage: Preferred for power distribution due to efficient voltage transformation and reduced losses over extended distances.
- DC Voltage: High-voltage direct current (HVDC) systems are gaining popularity for transmitting electricity over long distances, particularly in renewable energy projects.
- Applications Across U.S. Industrial and Energy Sectors
- AC Voltage Applications:
- Power distribution in industrial zones, manufacturing facilities, and business centers.
- Large-scale infrastructure projects and construction sites.
- Residential and commercial electrical systems.
- DC Voltage Applications:
- Renewable energy plants (solar and wind farms).
- Data centers and telecommunications.
- EV charging stations and battery storage facilities.
Transformers and Their Role in Managing AC and DC Voltage
Transformers are vital for adjusting voltage levels to ensure efficient energy transmission and industrial applications across the U.S.
AC Transformers
- Step-Up Transformers: Increase voltage for long-distance power transmission across regions.
- Step-Down Transformers: Lower voltage levels for industrial and commercial applications.
- Distribution Transformers: Provide stable voltage for residential and commercial areas.
DC Power Conversion Systems
- Rectifiers: Convert AC to DC for battery storage and electronic applications.
- Inverters: Convert DC to AC for seamless integration with the national power grid.
- HVDC Converters: Optimize long-distance power transmission, particularly for offshore wind farms and interstate power trading.
Impact on the U.S. Industrial and Energy Sectors
The U.S. industrial expansion and clean energy transition rely on strategic AC and DC voltage management. Efficient use of transformers and smart grid technology enhances stability, sustainability, and energy security.
Renewable Energy and Sustainability
With significant investment in renewable energy, particularly solar and wind power, DC voltage management is becoming a key focus. Solar farms generate DC electricity, which requires conversion to AC for grid distribution, highlighting the importance of advanced inverter and transformer technologies.
Industrial and Commercial Power Needs
Manufacturing plants, oil refineries, and infrastructure projects primarily operate on AC voltage. Meanwhile, automation systems, backup power solutions, and next-generation battery technologies increasingly rely on DC voltage integration. Balancing both systems efficiently ensures uninterrupted operations and long-term energy resilience.
Future Trends in AC and DC Power Systems in the U.S.
- Expansion of HVDC Technology
The U.S. is scaling HVDC transmission to optimize power efficiency, enhance renewable energy adoption, and facilitate interstate electricity trading.
- Smart Grid Development
AI-driven grid monitoring and automated voltage regulation are revolutionizing nationwide power distribution, boosting reliability and efficiency.
- Growth of Electric Vehicles (EVs)
With an increasing transition toward electric mobility, DC fast-charging infrastructure is expanding, supporting sustainable transportation nationwide.
Conclusion
The U.S. industrial and energy sectors depend on a strategic combination of AC and DC voltage systems to drive efficiency, sustainability, and economic growth. While AC voltage dominates power distribution, DC voltage is crucial in renewable energy integration, EV development, and advanced grid solutions. Transformer technologies, smart power management systems, and innovative energy infrastructure are pivotal for ensuring a stable and sustainable energy future in the United States.




No comment