Introduction
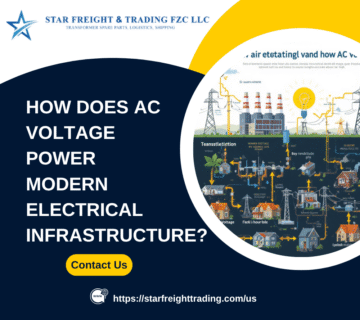
The United States operates one of the world’s largest and most complex electrical grids, powering everything from major industrial plants to suburban neighborhoods. At the heart of this vast infrastructure are transformers—devices that adjust voltage levels to support safe, efficient, and reliable energy transmission and distribution.
From high-voltage transmission lines crossing states to renewable energy plants and local substations, transformer technology plays a critical role in maintaining the stability and resilience of America’s power supply. This article explores how different types of transformers support the U.S. electrical infrastructure.
1. Power Transformers: The Backbone of Long-Distance Transmission
Power transformers are essential for transferring electricity from generation sources to load centers across vast distances.
Role in the U.S. Grid:
-
Step-up transformers at generation stations (nuclear, gas, hydro, solar) increase voltage for efficient transmission.
-
Step-down transformers at substations reduce voltage levels for local distribution.
-
Vital for reducing energy loss across high-voltage interstate transmission lines.
Given the size and geographic diversity of the U.S., power transformers are foundational for maintaining efficiency and reliability across the grid.
2. Distribution Transformers: Delivering Localized, Safe Power
Once electricity reaches urban or rural distribution points, distribution transformers reduce voltage for end-use in homes, businesses, and institutions.
How They Power America:
-
Deliver electricity at safe voltage levels to neighborhoods, schools, hospitals, and industries.
-
Found in utility poles, underground vaults, and pad-mounted units.
-
Ensure consistent service across commercial zones, residential areas, and critical infrastructure.
With growing demand from electric vehicles, smart homes, and data centers, distribution transformers are more important than ever in the U.S.
3. Oil-Immersed Transformers: High Performance in Heavy-Duty Applications
Oil-immersed transformers are commonly used throughout the U.S. power sector for their durability and cooling efficiency.
Why They’re Widely Used:
-
Ideal for outdoor substations and high-load applications.
-
Provide reliable cooling using insulating oil—suitable for demanding conditions.
-
Common in utility networks, industrial facilities, and energy infrastructure.
Their ability to manage large loads makes them a staple for long-term grid reliability and resilience.
4. Dry-Type Transformers: Fire-Safe and Maintenance-Friendly
Dry-type transformers, using air or resin insulation, are preferred in indoor or high-safety environments.
Popular Applications in the U.S.:
-
Schools, hospitals, data centers, and commercial buildings.
-
Urban developments and environmentally sensitive areas.
-
Renewable energy installations requiring low-maintenance components.
These transformers are favored where fire resistance, low environmental impact, and indoor compatibility are essential.
5. Smart Transformers: Supporting Grid Modernization and Automation
As the U.S. modernizes its aging grid infrastructure, smart transformers are being deployed to enable automation, real-time data collection, and remote management.
Benefits for the U.S. Energy System:
-
Enhance energy efficiency through demand-side management.
-
Enable predictive maintenance and rapid fault detection.
-
Critical to smart grids and microgrid systems being adopted across states.
Smart transformers play a pivotal role in ensuring the grid adapts to evolving energy needs and challenges.
6. Renewable Energy Transformers: Integrating Wind, Solar & Storage
The U.S. is accelerating its transition to renewable energy, with large-scale solar farms, wind farms, and battery storage becoming common across many states.
How They Aid the Transition:
-
Convert and balance energy from solar panels, wind turbines, and battery storage.
-
Ensure compatibility with the national grid.
-
Help maintain voltage stability in hybrid systems combining traditional and renewable power.
These specialized transformers are instrumental in meeting federal and state clean energy targets and reducing carbon emissions.
Conclusion
The U.S. electrical supply relies on a diverse range of transformer types—each serving a specific role in power generation, transmission, distribution, and modernization. Power transformers manage long-distance, high-voltage transmission, while distribution transformers ensure safe delivery to end users. Oil-immersed and dry-type transformers provide environmental and safety flexibility, while smart and renewable energy transformers are driving the future of a more intelligent, sustainable grid.
By investing in the right transformer technologies, the United States can continue to strengthen its power infrastructure, improve resilience, and meet the energy demands of tomorrow.




No comment